This study presents the new version 8 middle atmosphere ozone retrieval for the Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS) instrument. MIPAS was a high resolution limb sounder on board the Envisat satellite that measured between 685 and 2410 cm-1. Between 2002 and 2004 MIPAS was operated at 0.025 cm-1 spectral resolution, but instrument subsystem issues led to a gap in the data and a subsequent reduction in its operating resolution to 0.0625 cm-1. MIPAS was operated in this reduced-resolution mode from 2005 until 2012, when contact with Envisat was lost. Nominal operations for MIPAS saw measurements made between 6 and 68 km; however MIPAS was regularly operated in middle- and upper-atmosphere sounding modes (just termed the middle atmosphere modes hereafter), mainly after 2005.
MIPAS retrievals from the nominal operation measurements have been previously updated to use the new version 8.03 level-1b spectra that provide improved gain calibration as compared to previous versions of the spectra. In this study, these new spectra are used to retrieve a new ozone product from the middle atmosphere sounding modes. The major difference between the retrievals from the nominal and middle atmosphere modes is the necessity of incorporating into the radiative transfer calculations the effect of non-local thermodynamic equilibrium (non-LTE). This new retrieval version also incorporates several modifications from prior versions, including a change to the ozone a priori, a revision of the non-LTE processes, and a revision to the atomic oxygen nighttime concentration. The resulting ozone products span from approximately 20 to 100 km and cover the period from 2005 until 2012.
In order to evaluate the new version 8 middle atmosphere ozone, comparisons have been made with coincident measurements from Global Ozone Monitoring by Occultation of Stars (GOMOS), Aura - Microwave Limb Sounder (Aura-MLS), Sounding of the Atmosphere using Broadband Emission Radiometry (SABER), Superconducting Submillimeter-Wave Limb-Emission Sounder (SMILES), and ACE-FTS. The coincidence criteria employed require that pairs of coincident measurements are made within 2 hours and 1000 km of each other. Additionally, as ozone experiences a significant diurnal cycle in the middle and upper atmosphere, comparisons with ACE-FTS are only performed with MIPAS observations with solar zenith angles between 88 and 92 degrees. The results of these comparisons for global mean ozone are shown in Figure 1. Note that ACE-FTS measurements are only compared during the day, and GOMOS measurements during the night.
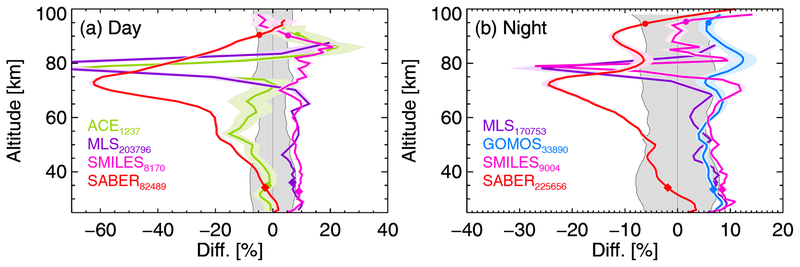
Figure 1: Comparisons of global mean daytime (left) and nighttime (right) ozone, expressed as a percent difference, between pairs of coincident measurements. The difference is calculated as MIPAS - Instrument and expressed as a fraction of MIPAS. The number of coincident measurements is indicated by the subscripts. The grey envelope shows the standard error of the mean differences.
Overall, the new version 8 MIPAS ozone product is found to be in good agreement with the comparisons datasets, with exception for SABER. Below 70 km, MIPAS is found to be high biased by about 5 to 8 %, as compared to Aura-MLS, SMILES, and GOMOS, and slightly low biased, by about 5 %, as compared to ACE-FTS. Agreement with ACE-FTS is poorer around the stratopause, but still within about 10 %. Larger differences are found with SABER, in excess of 60 % near 70 km; however a distinct high bias has been previously found for ozone from SABER. Above 80 km, the small magnitude of the ozone concentrations leads to noisier comparison profiles, but agreement remains typically within 10 to 20 %.
